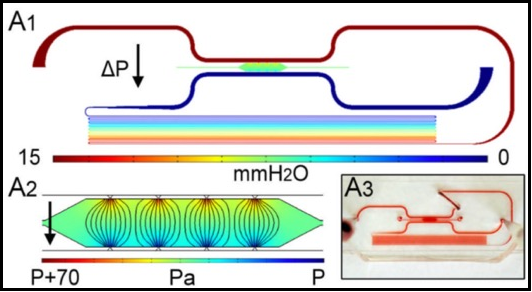
We report the first demonstration of a microfluidic platform that captures the full physiological range of mass transport in 3-D tissue culture. The basis of our method used long microfluidic channels connected to both sides of a central microtissue chamber at different downstream positions to control the mass transport distribution within the chamber. Precise control of the Péclet number (Pe), defined as the ratio of convective to diffusive transport, over nearly five orders of magnitude (0.0056 to 160) was achieved. The platform was used to systematically investigate the role of physiological mass transport on vasculogenesis. We demonstrate, for the first time, that vasculogenesis can be independently stimulated by interstitial flow (Pe > 10) or hypoxic conditions (Pe < 0.1), and not by the intermediate state (normal living tissue). This simple platform can be applied to physiological and biological studies of 3D living tissue followed by pathological disease studies, such as cancer research and drug screening.
Full range physiological mass transport control in 3D tissue cultures