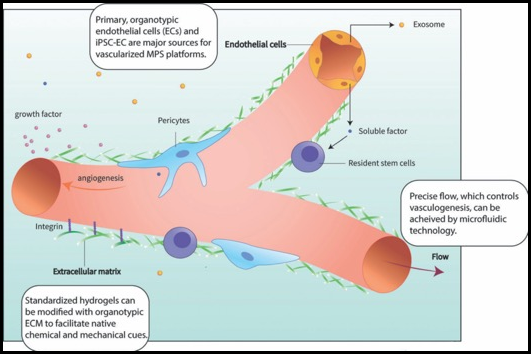
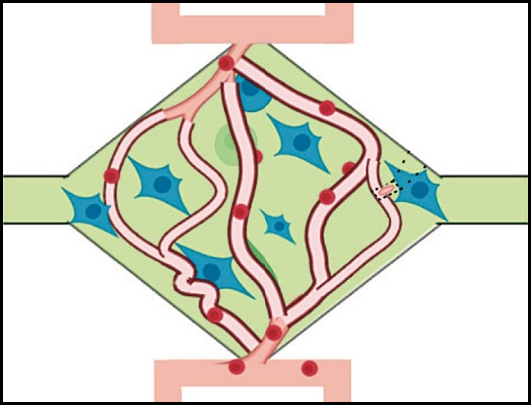
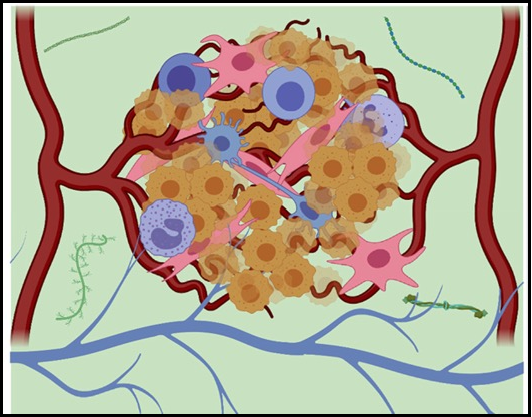
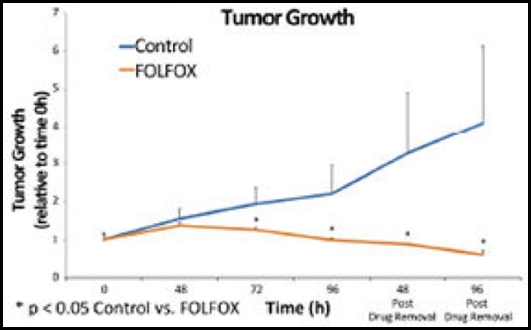
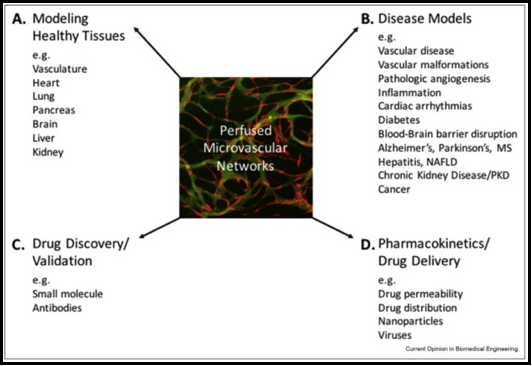
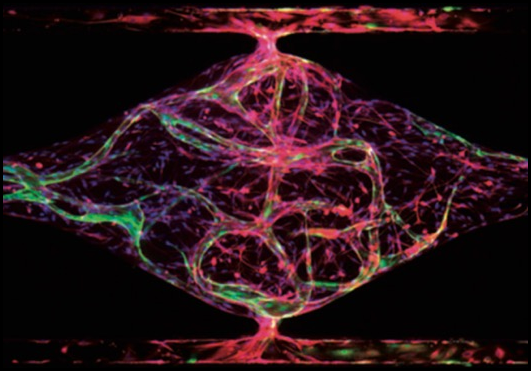
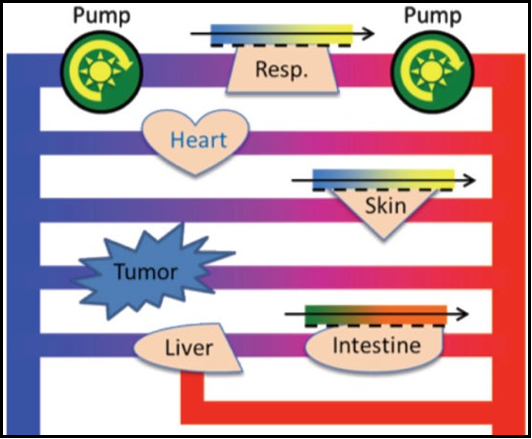
The vascular niche in next generation microphysiological systems
In recent years, microphysiological system (MPS, also known as, organ-on-a-chip or tissue chip) platforms have emerged with great promise to improve the predictive capacity of preclinical modeling thereby reducing the high attrition rates when drugs move into trials. While their designs can vary quite significantly, in general MPS are bioengineered in vitro microenvironments that recapitulate key functional …
The vascular niche in next generation microphysiological systems Read More »